Donate Blood & Save a Life
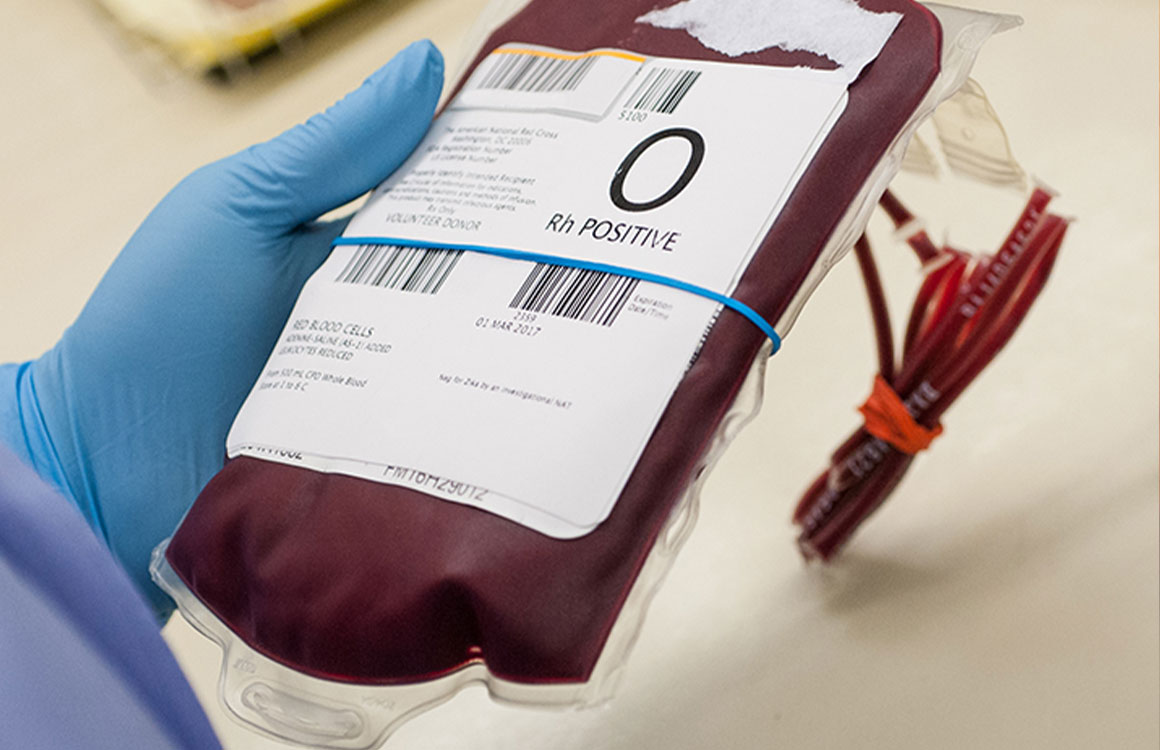
A blood donation occurs when a person voluntarily has blood drawn and used for transfusions and/or made into biopharmaceutical medications by a process called fractionation (separation of whole blood components). Donation may be of whole blood, or of specific components directly (apheresis). Blood banks often participate in the collection process as well as the procedures that follow it.
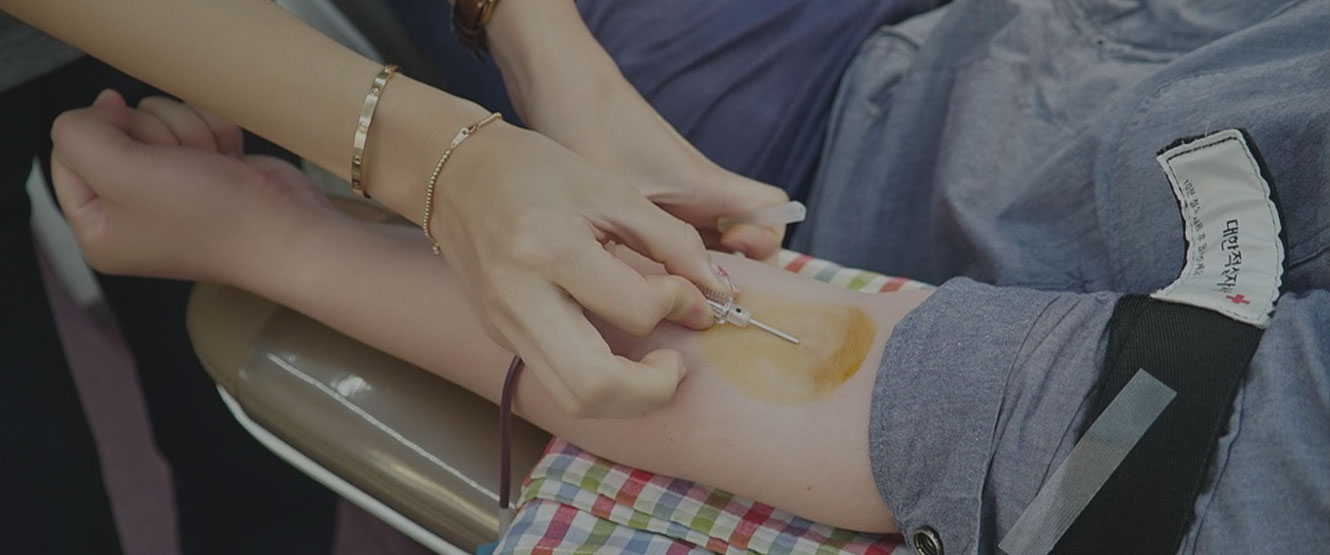
Donate Blood & Save a Life
Potential donors are evaluated for anything that might make their blood unsafe to use. The screening includes testing for diseases that can be transmitted by a blood transfusion, including HIV and viral hepatitis. The donor must also answer questions about medical history and take a short physical examination to make sure the donation is not hazardous to his or her health. How often a donor can donate varies from days to months based on what component they donate and the laws of the country where the donation takes place. For example, in the United States, donors must wait 56 days (eight weeks) between whole-blood donations but only seven days between platelet apheresis donations and twice per seven-day period in plasmapheresis.